Introduction to OpenACC Programming Model (C/C++ and Fortran)
Copyright (c) E. Krishnasamy, 2013-2021 UL HPC Team <hpc-sysadmins@uni.lu>
Objectives
- Understanding the OpenACC programming model
- How to use some of the directives from OpenACC to parallelize the code
- compute constructs, loop constructs, data clauses
- Implementing OpenACC parallel strategy in C/C++ and FORTRAN programming languages
- Simple mathematical examples to support and understand the OpenACC programming model
- Finally, show you how to run these examples using Iris cluster (ULHPC) - both interactively and using a batch job script
Prerequisite:
- C/C++ and/or FORTRAN languages
- OpenMP or some basic parallel programming concept (advantage not necessary)
Important: PRACE MOOC
NOTE: this lecture is limited to just 45 min, it only covers very basic tutorial about OpenACC. To know more about (from basic to advanced) CUDA programming and OpenACC programming model, please refer to PRACE MOOC GPU Programming for Scientific Computing and Beyond - Dr. Ezhilmathi Krishnasamy
Pre-requisites
Ensure you are able to connect to the UL HPC clusters.
In particular, recall that the module command is not available on the access frontends. For all tests and compilation, you MUST work on a computing node
Now you'll need to pull the latest changes in your working copy of the ULHPC/tutorials you should have cloned in ~/git/github.com/ULHPC/tutorials (see "preliminaries" tutorial)
(access)$ cd ~/git/github.com/ULHPC/tutorials
(access)$ git pull
Now configure a dedicated directory ~/tutorials/openacc for this session
# return to your home
(access)$ mkdir -p ~/tutorials/openacc
(access)$ cd ~/tutorials/openacc
# create a symbolic link to the top reference material
(access)$ ln -s ~/git/github.com/ULHPC/tutorials/gpu/openacc/basics ref.d # Symlink to the reference tutorial material
# copy / synchronize a copy of the exercises
(access)$ rsync -avzu ref.d/exercises . # DO NOT forget the trailing .
Advanced users (eventually yet strongly recommended), create a Tmux session (see Tmux cheat sheet and tutorial) or GNU Screen session you can recover later. See also "Getting Started" tutorial .
Connect to Iris cluster and get an interactive GPU job
See also GPU jobs documentation.
$ ssh iris-cluster # The only cluster featuring GPU
$ si-gpu -G 1 --ntasks-per-node 1 -c 7 -t 00:30:00 # (eventually) --reservation=hpcschool-gpu
Load the OpenACC compiler (PGI)
$> module spider pgi
$> module load compiler/PGI/19.10-GCC-8.3.0-2.32
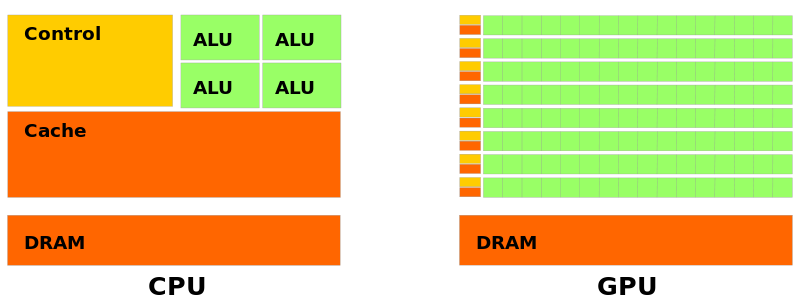
Difference between CPU and GPU
CPU vs GPU
- CPU frequency is higher compared to GPU
- But GPU can run many threads in parallel compared to CPU
- On the GPU, the cores are grouped and called "Streaming Multiprocessor - SM"
- Even on the Nvidia GPU, it has a "Tensor Process Unit - TPU" to handle the AI/ML computations in an optimized way
- GPUs are based on the "Single Instruction Multiple Threads"
- Threads are executed in a group on the GPU, typically they have 32 threads This is called "warps" on the Nividia GPU and "wavefronts" on the AMD GPU
CPU vs GPU
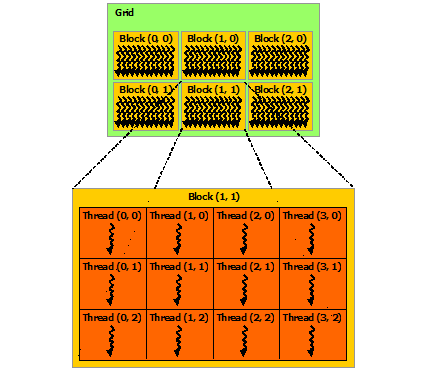
Thread Hierarchy
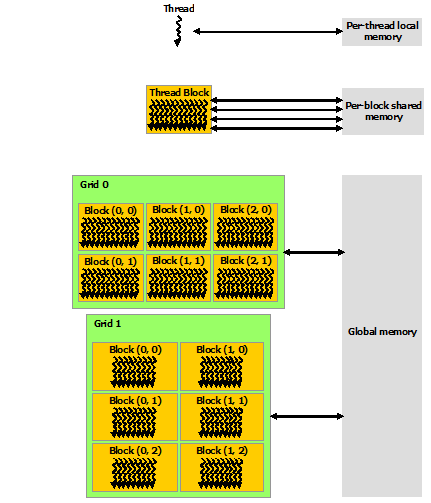
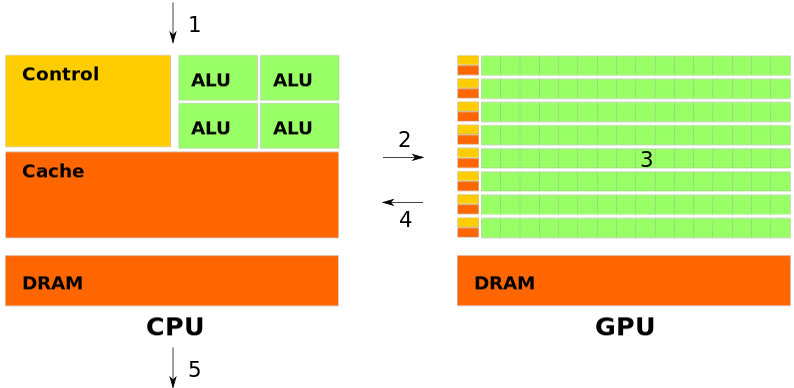
How GPUs are used for computations
- Step 1: application preparation, initialize the memories on both CPU and GPU
- Step 2: transfer the data to GPU
- Step 3: do the computation on the GPU
- Step 4: transfer the data back to the CPU
- Step 5: finalize the application and delete the memories on both CPU and GPU
OpenACC
Few points about OpenACC
- OpenACC is not GPU programming
- OpenACC is expressing the parallelism in your code
- OpenACC can be used in both Nvidia and AMD GPUs
- “OpenACC will enable programmers to easily develop portable applications that maximize
the performance and power efficiency benefits of the hybrid CPU/GPU architecture of
Titan.”
- Buddy Bland, Titan Project Director, Oak Ridge National Lab
- “OpenACC is a technically impressive initiative brought together by members of the
OpenMP Working Group on Accelerators, as well as many others. We look forward to
releasing a version of this proposal in the next release of OpenMP.”
- Michael Wong, CEO OpenMP Directives Board
Ways to accelerate applications on the GPU
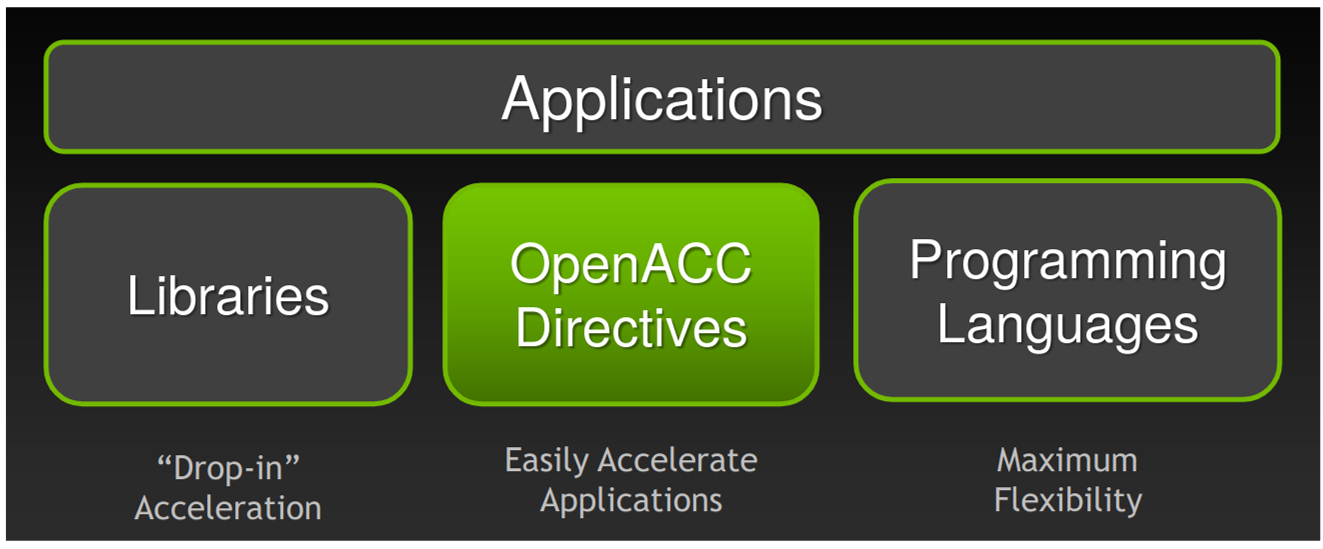
Ways to accelerate applications on the GPU
- Libraries: easy to use with very limited knowledge with GPU programming
- cuBLAS, cuFFT, CUDA Math Library, etc.
- Directive based programming model: will accelerate the application
with using directives in the existing code
- OpenACC and OpenMP (might be applicable in the future)
- Programming languages: low level programming languages that will
further optimize the application on the accelerator
- CUDA, OpenCL, etc.
Compilers and directives (only few of them listed in here)
- OpenACC is supported by the Nvidia, PGI, GCC, and HPE Gray (only for FORTRAN) compilers
- Now PGI is part of Nvidia, and it is available through Nvidia HPC SDK
- Compute constructs:
- parallel and kernel
- Loop constructs:
- loop, collapse, gang, worker, vector, etc.
- Data management clauses:
- copy, create, copyin, copyout, delete and present
- Others:
- reduction, atomic, cache, etc.
- More information about the OpenACC directives can be found in here
Basic programming structure
// C/C++
#include "openacc.h"
#pragma acc <directive> [clauses [[,] clause] . . .] new-line
<code>
!! Fortran
use openacc
!$acc <directive> [clauses [[,] clause] . . .]
<code>
Compute and loop constructs in OpenACC
kernels in C/C++
// Hello_World.c | // Hello_World_OpenACC.c
void Print_Hello_World() | void Print_Hello_World()
{ | {
| #pragma acc kernels
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) | for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{ | {
printf("Hello World!\n"); | printf("Hello World!\n");
} | }
} | }
- compilation:
pgcc -fast -Minfo=all -ta=tesla -acc Hello_World.c- The compiler will already give much info; what do you see?
$> pgcc -fast -Minfo=all -ta=tesla -acc Hello_World.c
Print_Hello_World:
6, Loop not vectorized/parallelized: contains call
main:
14, Print_Hello_World inlined, size=4 (inline) file Hello_World.c (5)
6, Loop not vectorized/parallelized: contains call
- Now add either kernels or parallel directives to vectorize/parallelize the loop
$> pgcc -fast -Minfo=all -ta=tesla -acc Hello_World_OpenACC.c
print_hello_world:
6, Loop is parallelizable
Generating Tesla code
6, !$acc loop gang, vector(32) ! blockidx%x threadidx%x
- As we can see above the loop is vectorized!.
kernels in FORTRAN
!! Hello_World.f90 | !! Hello_World_OpenACC.f90
subroutine Print_Hello_World() | subroutine Print_Hello_World()
integer :: i | integer :: i
| !$acc kernels
do i = 1, 5 | do i = 1, 5
print *, "hello world" | print *, "hello world"
end do | end do
| !$acc end kernels
end subroutine Print_Hello_World | end subroutine Print_Hello_World
- Compile the Hello_World.f90 and compiler tells us that the loop is not vectorized/parallelized.
$> pgfortran -fast -Minfo=all -ta=tesla -acc Hello_World.f90
print_hello_world:
5, Loop not vectorized/parallelized: contains call
- Now run the Hello_World_OpenACC.f90 either using kernels or parallel and we can already notice that loop is vectorized/parallelized.
$> pgfortran -fast -Minfo=all -ta=tesla -acc Hello_World_OpenACC.f90
print_hello_world:
6, Loop is parallelizable
Generating Tesla code
6, !$acc loop gang, vector(32) ! blockidx%x threadidx%x
Note: this above example is to show you how to create the parallel region using parallel and kernels and it quite useful when you have a multiple regions need to be prallelized. However, the above example has just one parallel region.
loop and data management clauses
for C/C++
- Here we can consider simple vector addition example for the OpenACC loop directive
// Vector_Addition.c | // Vector_Addition_OpenACC.c
float * Vector_Addition | float * Vector_Addition
(float *a, float *b, float *c, int n) | (float *a, float *b, float *c, int n)
{ | {
| #pragma acc kernels loop
| copyin(a[:n], b[0:n]) copyout(c[0:n])
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) | for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{ | {
c[i] = a[i] + b[i]; | c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
} | }
return c; |
} | }
- The loop will parallelize the for loop plus also accommodate other OpenACC clauses, for example here copyin and copyput.
- The above example needs two vectors to be copied to GPU and one vector needs to send the value back to CPU.
- copyin will create the memory on the GPU and transfer the data from CPU to GPU.
- copyout will create the memory on the GPU and and transfer the data from GPU to CPU.
for FORTRAN
!! Vector_Addition.f90 | !! Vector_Addition_OpenACC.f90
module Vector_Addition_Mod | module Vector_Addition_Mod
implicit none | implicit none
contains | contains
subroutine Vector_Addition(a, b, c, n) | subroutine Vector_Addition(a, b, c, n)
!! Input vectors | !! Input vectors
real(8), intent(in), dimension(:) :: a | real(8), intent(in), dimension(:) :: a
real(8), intent(in), dimension(:) :: b | real(8), intent(in), dimension(:) :: b
real(8), intent(out), dimension(:) :: c | real(8), intent(out), dimension(:) :: c
integer :: i, n | integer :: i, n
| !$acc kernels loop copyin(a(1:n), b(1:n))
| copyout(c(1:n))
do i = 1, n | do i = 1, n
c(i) = a(i) + b(i) | c(i) = a(i) + b(i)
end do | end do
| !$acc end kernels
end subroutine Vector_Addition | end subroutine Vector_Addition
end module Vector_Addition_Mod | end module Vector_Addition_Mod
- Now compile and run the above code as we did previously.
reduction clause in vector addition
for C/C++
// Vector_Addition.c | // Vector_Addition_OpenACC.c
float * Vector_Addition | float * Vector_Addition
(float *a, float *b, float *c, int n) | (float *a, float *b, float *c, int n)
{ | { float sum=0;
| #pragma acc kernels loop
| reduction(+:sum) copyin(a[:n], b[0:n]) copyout(c[0:n])
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) | for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{ | {
c[i] = a[i] + b[i]; | c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
} | sum+=c[i];
return c; | }
} | }
for FORTRAN
!! Vector_Addition.f90 | !! Vector_Addition_Reducion_OpenACC.f90
module Vector_Addition_Mod | module Vector_Addition_Mod
implicit none | implicit none
contains | contains
subroutine Vector_Addition(a, b, c, n) | subroutine Vector_Addition(a, b, c, n)
!! Input vectors | !! Input vectors
real(8), intent(in), dimension(:) :: a | real(8), intent(in), dimension(:) :: a, b
real(8), intent(in), dimension(:) :: b | real(8):: sum=0
real(8), intent(out), dimension(:) :: c | real(8), intent(out), dimension(:) :: c
integer :: i, n | integer :: i, n
| !$acc kernels loop reduction(+:sum)
| copyin(a(1:n), b(1:n)) copyout(c(1:n))
do i = 1, n | do i = 1, n
c(i) = a(i) + b(i) | c(i) = a(i) + b(i)
end do | sum = c(i)
| end do
end subroutine Vector_Addition | !$acc end kernels
end module Vector_Addition_Mod | end subroutine Vector_Addition
end module Vector_Addition_Mod
- reduction clause is needed when we want to sum the array or any counting inside the parallel region; this will increase the performance and avoid the error in the total sum.
- The above example shows how to use them in C/C++ and FORTRAN languages.






